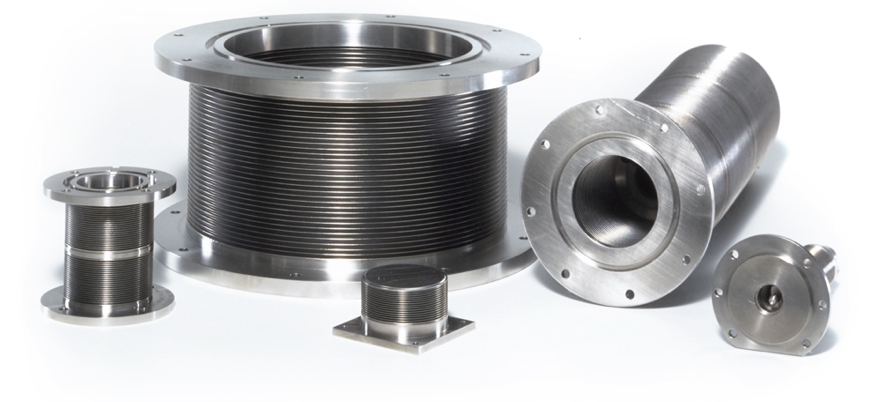
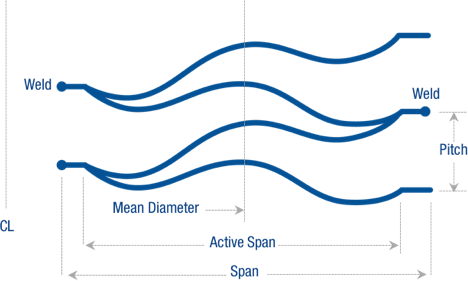
- GTAW & CO2 laser welding
- Thickness (0.001 to 0.025 inches)
- Sizes, diameters (0.125 to 23 inches)
- Round and non-round
- Materials
- Stainless steels
- High nickel alloys
- Titanium
- Mass spectrometer leak tight
- 1 × 10-10 std cc/sec He capability (1 cc in 320 years)
- Zero leakage dynamic seal
2025 SMB Exhibitions
Learn More